Consumption of sugar
Introduction
Sugar topic is very known. You can get a lot info about harmful impact of it. Nevertheless, very little amount of people know what sugar is and how it is processed in our bodies.
This article will help you to obtain very new, but simple attitude to all foods, especially those having added sugar.
Sugar is made from all healthy and unhealthy carbohydrates
This statement is very important to understand from the very beginning. Usually we call sugar the sweetness which is given to the products by added processed sugar of natural, like lactose and fructose.
We used to think as well, that sugar is something very much needed to our brains to function, especially when minds have to work very hard (during learning, thinking, making science etc.). But let us check what sugar is and how it is processed in the body.
Sugar is made of two molecules – glucose and fructose. Fructose is a natural sugar, which is found in fruits and veggies. Glucose – you know, is something which is regularly (we hope) checked in human’s blood during the health prophylactics. So, glucose is something regular in our blood. Blood must contain glucose, because it is a fuel for cells. By the way, fuel for all cells of the body, not only the brain.
You know, we usually call glucose in blood – a sugar. If glucose has to be present, means sugar has to be present in the blood – why then everybody says sugar is harmful?
Let’s find out, how glucose appears in the blood. It is very important to understand, that blood sugar level is not a level of the sugar consumed with fruits, sweet beverages, deserts or alcohol. Glucose is made from all carbohydrates we consume. All carbohydrates, no matter if healthy ones or not, no matter if they come from added sugar, natural sugar, vegetables, corns, wholegrains etc – are tuned into glucose in the blood. Later, glucose is absorbed by the cells and energy is produced in cells like fuel.
Which carbohydrates are healthy and unhealthy?
We know now, that all carbs (carbohydrates) turn into sugar in our blood. How to know, which one will help our body with energy, and which one will fuel cells but will damage them too?
It’s all about the way carbohydrates are processed in our body. The higher amount of carbs and the quicker they are turned into glucose in our blood, the more unhealthier carbs are.
From the article about reading the labels, you could find out, that fiber of grains helps to slow down processing of sugar in the food made of grains. The same happens when we consume vegetables and whole fruits, which are high enough in fiber.
How sugar is processed in the body?
Carbohydrates turn into glucose in the blood. As soon as we consume various food containing carbs, depending of their type and food which comes together, for instance food with fiber, fats and proteins – carbs are more quickly or more slowly are processed and fill the blood with glucose.
Please look at the picture No. 7 to demonstrate bodies rection on different carbs from the various good. The green lines show limits of the norm of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Obviously, it can’t be 0, but it shall not exceed some upper level too (upper norms may vary).
When processed sugar is consumed with sugary food and drinks, it fills up blood with high amount of glucose in a very short time – the red peak in the picture. The body answer is always a production of hormone insulin (produced by pancreas) which has its primary role to help cells consume glucose.
Insulin helps lower glucose levels in the blood. The process may be compared to a fire in the place. The fire is very high glucose level. Because high glucose levels mean very dense blood (sweet blood), which struggles to move in our vessels – the higher density the more difficult transportation of blood is. Insulin lowers the levels of the glucose and blood density returns to normal. The more insulin is produced – the quicker process of cell sugar consumption is, the quicker glucose level is lowered.
However, it does not mean, that high insulin level is healthy. Higher than needed insulin levels in the blood arise inflammations in the cells of vessels and makes our blood system suffer. When too much sugar consumed (red peak), and too much insulin is produced, it lowers the glucose level in the blood to the level below norms in 20-30 mins. That is why sweets will never bring a feeling of satiety. Lower than normal glucose level means cells are hungry, they lack fuel. So the body starts feeling unsatisfied and need to refuel.
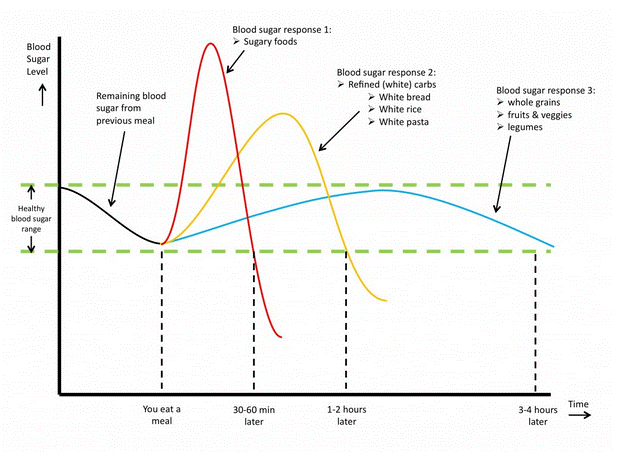
If you look at the yellow peak in the same picture, you will find that body reacts in a very similar way as in the case of sugar (red peak) to processed not whole grain products.
The blue line demonstrates recommended food to assure that glucose levels in the blood would stay in norm, the body would not be in lack of fuel, satiety would last longer.